SwiftUI TextField Memory Leak on iOS 17+ - Analysis
A critical memory leak has been discovered in SwiftUI's TextField implementation on iOS 17 and later versions. While originally found in SwiftUI, this bug actually affects all UITextField instances across both SwiftUI and UIKit due to a fundamental issue in the AutoFillUI framework.
However, the impact is significantly more severe in SwiftUI applications because SwiftUI TextFields can hold references to large amounts of data through EnvironmentObjects. This article provides a deep analysis of the problem, its root cause, and practical workarounds.
The Problem
When a SwiftUI TextField becomes the first responder and the user navigates away from that view, the TextField and its associated resources are not properly released from memory. This leak persists until another responder becomes the first responder, triggering the delayed cleanup.
Affected Code Pattern
struct ContentView: View {
@State var text = ""
var body: some View {
TextField("Test", text: $text)
}
}
Even this simple TextField implementation will leak memory when the view is dismissed after the TextField has been activated.
Root Cause Analysis
The memory leak is caused by improper resource cleanup in iOS 17's AutoFillUI framework:
The Culprit: AFUITargetDetectionController
The leak originates from AFUITargetDetectionController in the AutoFillUI.framework, which maintains a strong reference to an autoFillGroup that isn't properly cleared when the TextField is dismissed.
The Complete Reference Chain
The memory leak involves a complex chain of strong references that prevents proper deallocation:

- TextField Activation: When a TextField becomes first responder,
AFUITargetDetectionControllercreates anautoFillGroup - View Dismissal: When the user navigates away, SwiftUI calls
resignFirstResponderand removes the TextField from its superview - Incomplete Cleanup: The
clearAutoFillGroupmethod is not triggered byresignFirstResponder - Memory Retention Chain: The complete reference chain that prevents deallocation:
AFUITargetDetectionController (AutoFillUI.framework)
↓ strongly retains
UITextField
↓ via traitCollection property
SwiftUIEnvironmentWrapper
↓ strongly retains
TypeElement (SwiftUI.PropertyList implementation detail)
↓ strongly retains
Your EnvironmentObject (e.g., DataModel)
Memory Graph Analysis
The following memory graph screenshots demonstrate the leak in action, showing how AFUITargetDetectionController retains the autoFillGroup and the entire object graph:
Memory Leak Evidence - AFUITargetDetectionController Retention: 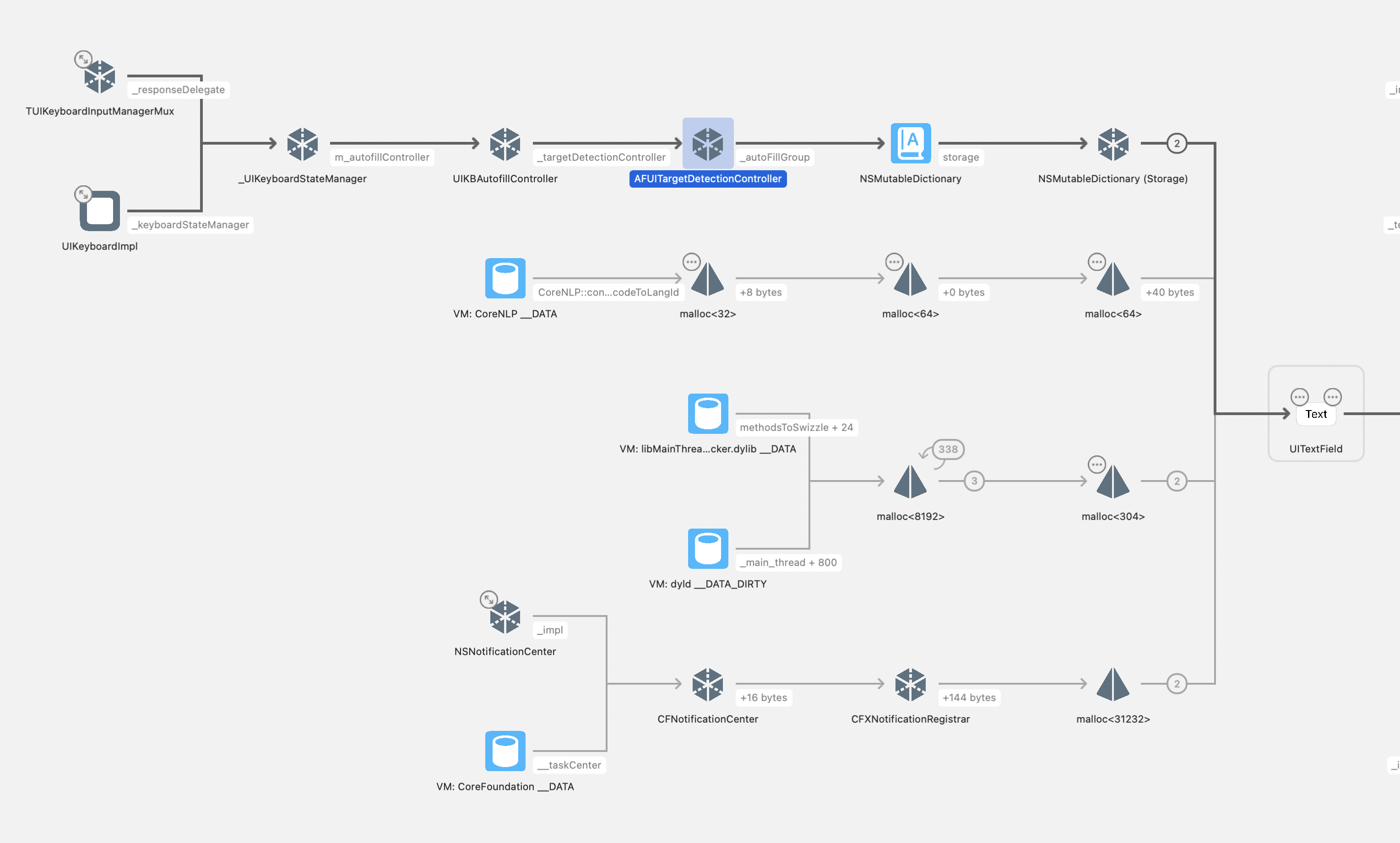
Detailed View of the Retention Chain: 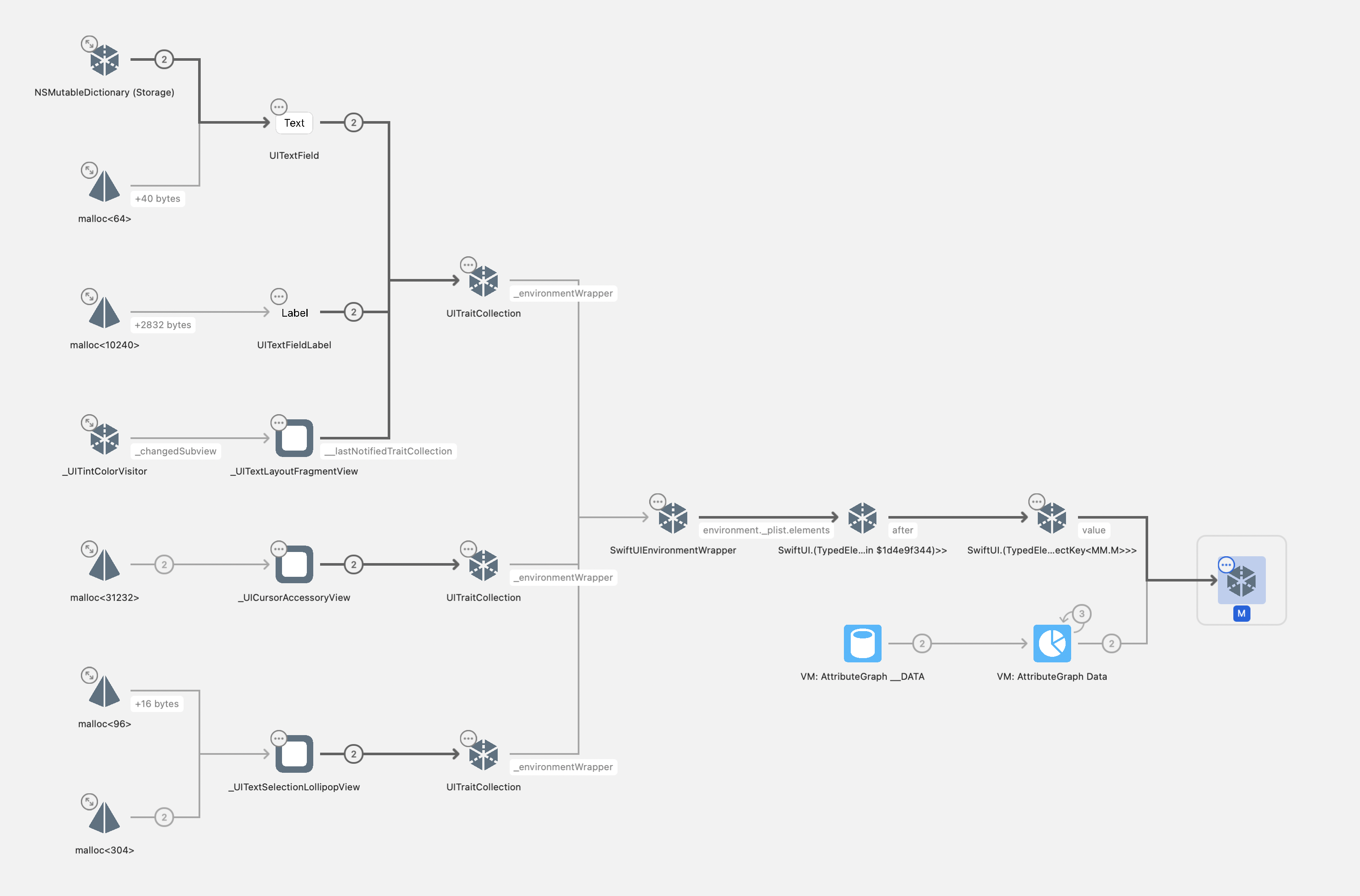
Both screenshots show the problematic state where the AFUITargetDetectionController keeps references alive. When the workaround is properly applied, these objects would be deallocated and you would see "LeakTestModel deallocated" printed in the console, indicating the memory has been properly released.
This means that any objects passed via .environmentObject() to a TextField will be leaked until the next keyboard source is triggered (e.g., another UITextField becomes first responder).
The Delayed Release
The leak is only resolved when:
- Another keyboard source is triggered (e.g., another UITextField becomes first responder)
- This triggers
[AFUITargetDetectionController clearAutoFillGroup] - Finally releasing the retained TextField and its associated objects
Impact and Scope
Affected Versions
- iOS 17.0 through iOS 26.0.x
- The bug was introduced with the AutoFillUI framework changes in iOS 17
- iOS 16.x is not affected as it lacks AFUITargetDetectionController
Fixed in iOS 26.1 Beta 3 (expected to ship with iOS 26.1)
SwiftUI vs UIKit Impact Differences
While this bug affects both SwiftUI and UIKit UITextField usage, the impact severity differs significantly:
UIKit Impact (Moderate)
- Traditional UIKit apps typically don't attach large object graphs to UITextField instances
- Memory leaks are usually limited to the TextField itself and basic associated objects
- Impact is generally manageable in most UIKit applications
SwiftUI Impact (Severe)
- SwiftUI TextField can hold references to massive object graphs via
.environmentObject() - Common patterns like view models, data stores, and complex state objects get leaked
- A single TextField can retain megabytes of data through environment object chains
- Multiple TextFields in navigation flows can compound the problem exponentially
Real-World Impact
Consider an app with EnvironmentObjects:
struct ContentView: View {
let model = DataModel()
@State private var text = ""
var body: some View {
TextField("Input", text: $text)
.environmentObject(model)
}
}
class DataModel: ObservableObject {
var data = Data() // Potentially large data
deinit {
print("DataModel deallocated") // This won't print!
}
}
In this scenario, the DataModel will remain in memory indefinitely until another keyboard source is triggered elsewhere in the app (e.g., another TextField becomes first responder).
Workaround Solutions
Solution 1: Use autocorrectionDisabled Modifier (Easiest)
The simplest way to avoid this bug is to use the autocorrectionDisabled modifier on your TextField:
struct ContentView: View {
@State var text = ""
var body: some View {
TextField("Test", text: $text)
.autocorrectionDisabled(true)
}
}
This prevents the AutoFillUI framework from interfering with the TextField's lifecycle, thus avoiding the memory leak entirely.
Credit: @ShikiSuen for discovering this solution
Solution 2: Trigger Manual Cleanup
The most reliable workaround involves manually triggering the cleanup mechanism:
override func viewDidAppear(_ animated: Bool) {
super.viewDidAppear(animated)
// Create a temporary TextField to trigger cleanup
let field = UITextField(frame: .zero)
view.addSubview(field)
field.becomeFirstResponder()
field.removeFromSuperview()
}
Solution 3: Implement in UIHostingController
For SwiftUI views embedded in UIKit:
class CleanupHostingController<Content: View>: UIHostingController<Content> {
override func viewDidAppear(_ animated: Bool) {
super.viewDidAppear(animated)
performCleanupWorkaround()
}
private func performCleanupWorkaround() {
let tempField = UITextField()
view.addSubview(tempField)
tempField.becomeFirstResponder()
tempField.resignFirstResponder()
tempField.removeFromSuperview()
}
}
Solution 4: Navigation-Based Cleanup
For navigation-heavy apps, implement cleanup when returning to parent views:
class NavigationController: UINavigationController {
override func popViewController(animated: Bool) -> UIViewController? {
let result = super.popViewController(animated: animated)
// Trigger cleanup after navigation
DispatchQueue.main.async { [weak self] in
self?.performTextFieldCleanup()
}
return result
}
private func performTextFieldCleanup() {
let tempField = UITextField()
view.addSubview(tempField)
tempField.becomeFirstResponder()
tempField.removeFromSuperview()
}
}
Complete Reproduction Case
Here's a complete example demonstrating the leak:
import SwiftUI
struct ContentView: View {
let model = LeakTestModel()
@State private var text = ""
var body: some View {
TextField("Test Input", text: $text)
.environmentObject(model)
}
}
class LeakTestModel: ObservableObject {
var data = Data(count: 1024 * 1024) // 1MB of data
deinit {
print("LeakTestModel deallocated")
}
}
class TestViewController: UINavigationController {
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
pushViewController(EntryViewController(), animated: false)
}
}
class EntryViewController: UIViewController {
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
view.backgroundColor = .white
navigationItem.rightBarButtonItem = UIBarButtonItem(
title: "Show TextField",
style: .plain,
target: self,
action: #selector(showTextField)
)
}
@objc func showTextField() {
let contentView = ContentView()
let hostingController = UIHostingController(rootView: contentView)
navigationController?.pushViewController(hostingController, animated: true)
}
}
When running this code: 1. Tap "Show TextField" 2. Tap in the TextField to activate it 3. Navigate back 4. Notice that "LeakTestModel deallocated" is never printed
Recommendations
For App Developers
- Implement Workarounds: Use the provided workaround solutions in production apps
- Monitor Memory Usage: Pay special attention to memory usage in views with TextFields
- Test Navigation Flows: Ensure memory is properly released in complex navigation scenarios
For Framework Developers
- Avoid Heavy EnvironmentObjects: Be cautious with large objects in TextField-containing views
- Consider Alternative Input Methods: For simple inputs, consider custom implementations
- Profile Memory Usage: Regular memory profiling is essential when using TextFields
Apple's Fix in iOS 26.1 Beta 3
Apple has addressed this memory leak in iOS 26.1 Beta 3, and the fix is expected to ship with iOS 26.1.
The Fix Details
The fix ensures that -[AFUITargetDetectionController clearAutoFillGroup] is now called at the correct time during the TextField lifecycle. Previously, this cleanup method was only triggered when another responder became first responder, causing the memory leak. With the fix, the cleanup happens properly when the TextField is dismissed.
Here's a debugger screenshot showing the correct cleanup sequence in iOS 26.1 Beta 3:
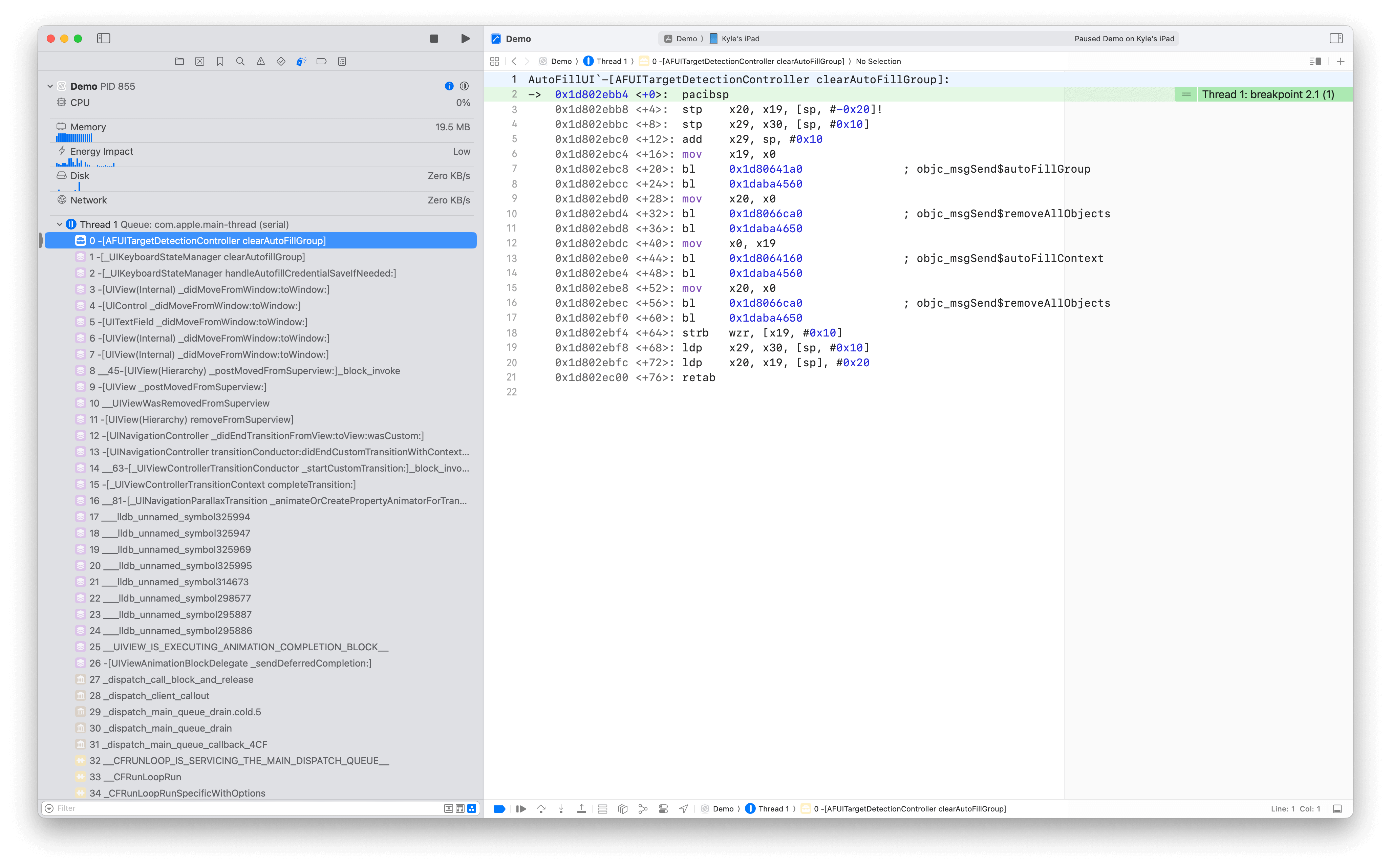
The screenshot demonstrates that clearAutoFillGroup is now invoked at the appropriate point in the view controller lifecycle, ensuring that the autoFillGroup and all associated objects are properly released when the TextField is dismissed.
Impact on Existing Apps
For apps targeting iOS 26.1 and later, the workarounds described in this article will no longer be necessary. However, if you need to support iOS 17.0 through iOS 26.0.x, you should continue using the workarounds to prevent memory leaks on those versions.
Apple Feedback and Resolution Status
This issue was reported to Apple via Feedback Assistant FB20302615 and has been fixed in iOS 26.1 Beta 3.
Version-Specific Recommendations
iOS 26.1+: The bug is fixed. No workarounds needed.
iOS 17.0 - iOS 26.0.x: The bug exists. Implement workarounds as described below.
iOS 16.x and earlier: Not affected by this bug.
Conclusion
This TextField memory leak represented a significant issue in iOS 17.0 through iOS 26.0.x that affected all SwiftUI applications using TextField. Apple has now addressed this bug in iOS 26.1 Beta 3, which is expected to ship with iOS 26.1.
The root cause was in the AutoFillUI framework's incomplete cleanup mechanism, specifically the AFUITargetDetectionController class not calling clearAutoFillGroup at the correct time. Apple's fix ensures this cleanup method is now properly invoked during the TextField lifecycle.
For developers supporting older iOS versions (17.0 - 26.0.x), continue implementing the workarounds described in this article. For apps targeting iOS 26.1 and later, you can rely on the system fix and remove the workarounds.